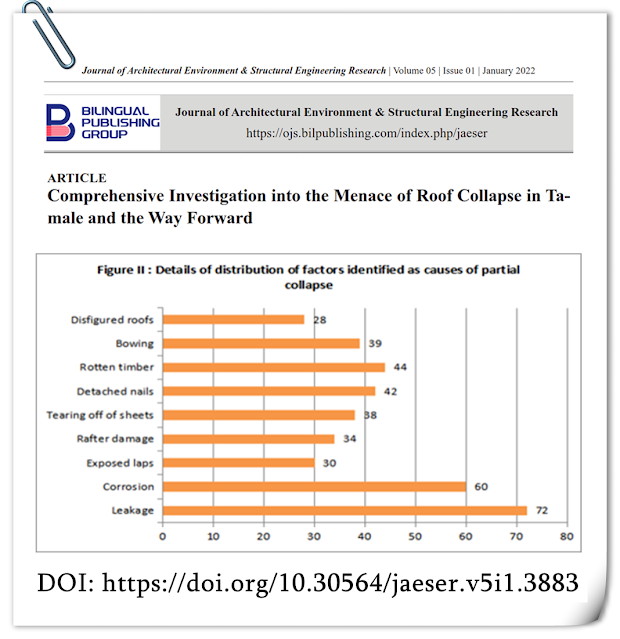
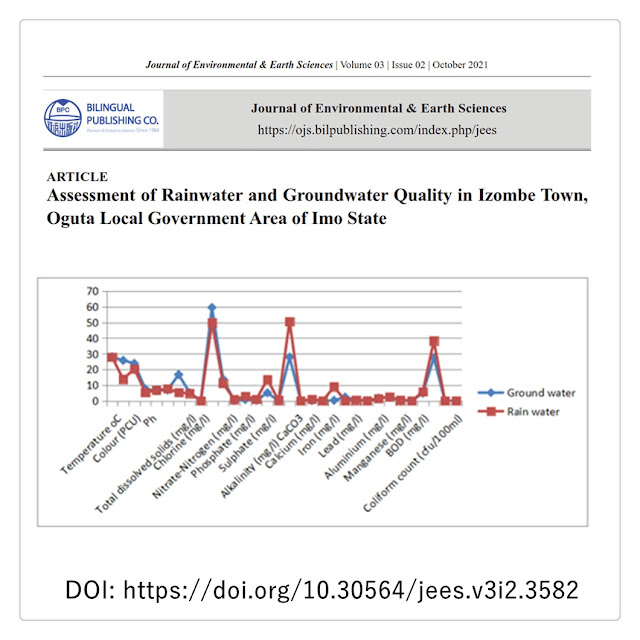
Towards Sustainable Living: From COP21 to COP26 and beyond

Towards Sustainable Living: From COP21 to COP26 and beyond DOI: https://doi.org/10.30564/jaeser.v5i1.4440 References [1] Drolet, J., 2015. Disasters in Social, Cultural and Political Context, International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences (Second Edition). pp. 478-484. [2] Christopher Rhodes, J., 2016. The 2015 Paris Climate Change Conference: COP21, Science Progress. 99(1), 97-104. [3] Collaboration – The Paris Rulebook, UN Climate Change Conference UK 2021. (Accessed November 16, 2021). [4] Dietz, L., Horve, P.F., Coil, D.A., et al., 2020. 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: Built environment considerations to reduce transmission. Msystems. 5, e00245-20.